Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM)
Under the Goods and Services Tax (GST), the general rule is that the supplier of goods or services is responsible for paying the tax. However, the Reverse Charge Mechanism shifts this responsibility to the recipient of the goods or services. This shift occurs in scenarios where the supplier is either unregistered under GST or falls into a specific category designated by the government. In such cases, the recipient of the supply is liable to pay GST directly to the government and report it in their GST returns.
RCM is applicable in the following situations:
Under Section 9(3) of the CGST Act: This section allows the government, based on recommendations from the GST Council, to specify categories of supplies where the recipient, rather than the supplier, is liable to pay GST. The government has issued notifications specifying certain goods and services that fall under this provision.
Under Section 9(4) of the CGST Act: This section stipulates that if a supplier who is not registered under GST provides taxable goods or services to a registered person, the recipient is responsible for paying the GST under RCM. In essence, if a registered recipient acquires goods or services from an unregistered supplier, the recipient must handle the GST payment.
Requirement of Issuing Tax Invoices for RCM Transactions
According to Section 31 of the CGST Act, 2017, a tax invoice must be issued for taxable supplies. The key provisions are:
For Goods: A tax invoice must be issued before or at the time of the removal of goods if the supply involves their movement, or at the time of delivery or making available of goods in other cases. The invoice should detail the description, quantity, value of goods, and the tax charged.
For Services: A tax invoice should be issued before or after the provision of services but within a prescribed period, detailing the description, value, and tax charged.
Despite the Reverse Charge Mechanism, the supply remains taxable, making the issuance of a tax invoice imperative.
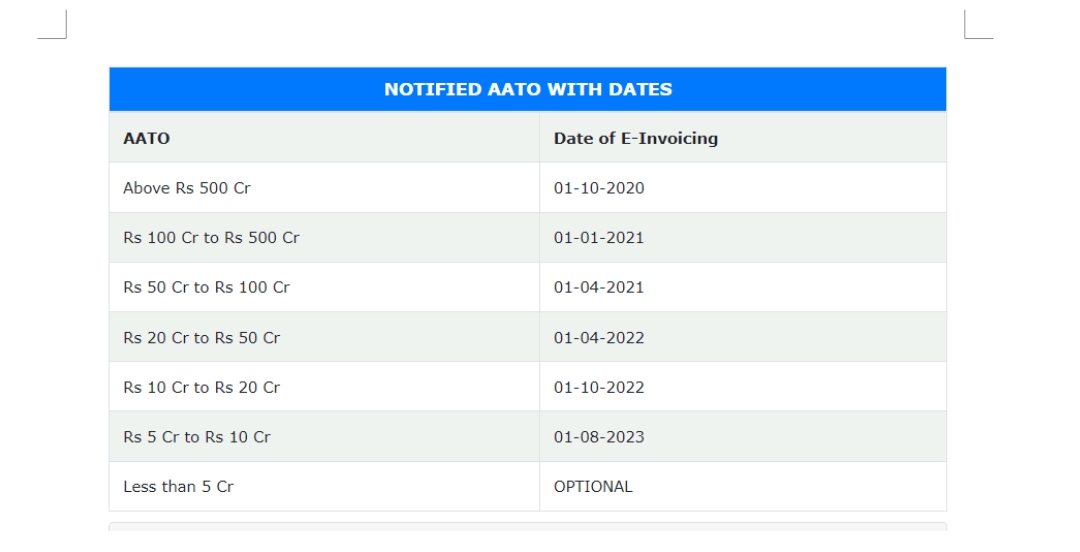
E-Invoicing Applicability to RCM Transactions
To understand e-invoicing applicability,
E-invoicing applies to GST registered persons whose aggregate turnover in any previous financial years (2017-18 to 2021-22) exceeded 5 Cr
E-Invoicing applicable toTaxable Business-to-Business sale of goods or services, Business-to-government sale of goods or services, exports, deemed exports, supplies to SEZ (with or without tax payment), stock transfers or supply of services to distinct persons, SEZ developers, and supplies under reverse charge covered by Section 9(3) of the CGST Act.
However e-Invoicing shall not be applicable to the following TransactionAny Business-to-Consumers (B2C) sales, Nil-rated or non-taxable or exempt B2B sale of goods or services, nil-rated or non-taxable or exempt B2C sale of goods or services, imports, high sea sales and bonded warehouse sales, Free Trade & Warehousing Zones (FTWZ), and supplies under reverse charge covered by Section 9(4) of the CGST Act.